Heat stress: Many recent studies has shown that cases of heat-related illness are increased in the last few years compare to the past. In countries like India deaths due to heat increased by 55% from 2017 to 2021 compared with 2000-2004. The number of deaths due to exposure to heat increased from 20,000 to 31,000 in this period. Globally 3.1 lakh people lost their life due to heat-related illness in the last 4 years which is alarming. In 2021 due to heat exposure, Indian lost 167.2 billion working hours which is very high. Because of global warming, the temperature of the earth is rising day by day, and illnesses related to heat will increase in the coming years. To save ourselves and our families from Heat stress knowledge of heat stress is required. Here in this article, our team provides details on heat stress along with first-aid measures and control measures.
What is Heat stress?
A situation where too much heat is absorbed by a person which causes stress, illness, or death. People who work in extreme heat or hot environments are always at risk of heat stress. Heat stress can also cause heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heat rashes, or heat stroke which may lead to death.
Heat stress occurs when the body cannot get relief from the excess heat. When this happens, the heart rate increases and the body’s core temperature rises

Who is exposed to Heat stress?
Any activities in which workers’ body temperature rises more than 100.4o F or 38o C can result in heat stress. Employees who are exposed to radiant heat, high air temperature, high humidity, working with hot objects, or strenuous physical activities in their workplace have a high potential for heat stress.
Example of workplaces where the risk of heat stress is high
- Ceramic industries (Kiln)
- Foundries
- Brick making industries
- Glass manufacturing
- Boiler operation
- Food kitchen
- Smelters
- Bakeries
- Steam turbine
- Mining
- Outdoor operation in summer
Common factors responsible for Heat stress
- Age, weight
- Metabolism
- Physical Fitness
- Dehydration
- Use of alcohol or drug
- Hypertension
- Working environments
- Types of clothing
- Colours of clothing (Dark colours absorb more heat)
Types of Heat Stress
- Heat Stroke
- Heat Exhaustion
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Heat Syncope
- Heat Cramps
- Heat Rash
1. Heat Stock:
Heat stock happens when the body mechanism fails to maintain (control) body temperature, resulting in permanent disability or death. Heat stock occurs due to long working hours in a hot environment
Symptoms of Heat Stock:
- Confusion
- Lack of sweating
- High body temperature (41o C or 105.8o F)
- Rapid pulse
- Weakness
- Loss of coordination
- Headache
- Seizure
- Coma
First Aid for Heat stock
- Called for Immediate medical treatment
- Shift worker to a cool and shady place and remove outer clothes
- Wet the worker’s body by applying water on his body and increasing air movement surrounding to him
2. Heat Exhaustion
In heat exhaustion, sufficient oxygen is not received by the brain, and the person becomes unconscious. This happens due to excessive loss of water or salt caused by sweating.
Symptoms of Heat Exhaustion:
- Thirst
- Vomiting
- Heavy sweating
- Increase body temperature
- Rapid Heart Rate
- Fatigue
- weakness
First Aid for Heat Exhaustion
- Immediately move the exposed person to a cool place
- Loose or remove clothes
- Call medical help
- Give shower (if possible, with cool water)
- Provide electrolytes or water
3. Rhabdomyolysis:
Rapid breakdown of muscle fibers due to exposure to high temperature or more physical work. Electrolytes and protein are discharged from the blood due to muscle breakdown, which damages the kidney or disturbs heartbeats. In many cases, the victim loses their lives due to rhabdomyolysis. It is diagnosed by blood test creatine kinase (muscle protein)
Symptoms of Rhabdomyolysis
- Muscle pain
- Muscle cramp
- Reduce work efficiency
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Body pain
- Dark colour urine
First Aid for Rhabdomyolysis
- Drink plenty of water which helps in recovering your kidney
- Take rest
- Keep your body hydrated
- Avoid sweating
4. Heat Syncope:
In Heat Syncope, the brain receives less amount of blood due to heat exposure, which results in a mild headache or fainting for some time. These conditions arise when a person works in a hot atmosphere for a long period & a large amount of his body fluid (body salt) is lost through sweating.
Heat Syncope is different from heat stock
- Light headache
- Dizziness
- Tunnel vision
- Weakness
- Loss of consciousness
- Vomiting
- Nausea
First Aid for Heat Syncope
- Patient recovered in 10 to 15 minutes
- Move in a cold atmosphere
- Remove extra clothes and use wet towels or ice bags
- Drink plenty of water or juice which contains salt
- If a person is unconscious measure blood pressure and heartbeats and provides CPR
5. Heat Cramps:
Heat cramps are most common in children and aged people. The main reason behind heat cramps is the loss of a large amount of water & salt or insufficient consumption of water or salt. Heat cramps occur in the abdomen, claves, back, and arms. It denotes an early sign of the heat stocks
Symptoms of Heat Cramps:
- Cramping on the back, abdomen, laves, or arms
- Fainting & headache
- Rashes on the skin (red bums)
- Itching
First Aid for Heat Cramps:
- Take rest
- Drink water juice or electrolyte
- Initiate some basic exercise & massage like stretching and massage at the affected muscle
- Avoid hard physical work for some hours after cramps have gone
- In case cramps are not gone within hours connect with doctors
6. Heat Rashes:
Heat rashes occur during long hours of work in hot and humid atmospheres. Skin rashes are done because sweat is trapped in the skin. In this, the skin becomes red because of small blisters or pimples.
Symptoms of Heat Rash
- Redness on neck, chest, breast, back, hand, and armpits
- Inflamed bums
- Itching
- Small blisters
First Aid for Heat Rash
- Normally, it will automatically disappear as the skin cooled
- Loosen clothes and provide a cool shower
- Avoid humid and hot atmospheres till recovered
- If rashes are not gone within 2-3 days connect with doctors
Controls for Heat stress
Always follow the hierarchy of control to avoid heat stress in the workplace
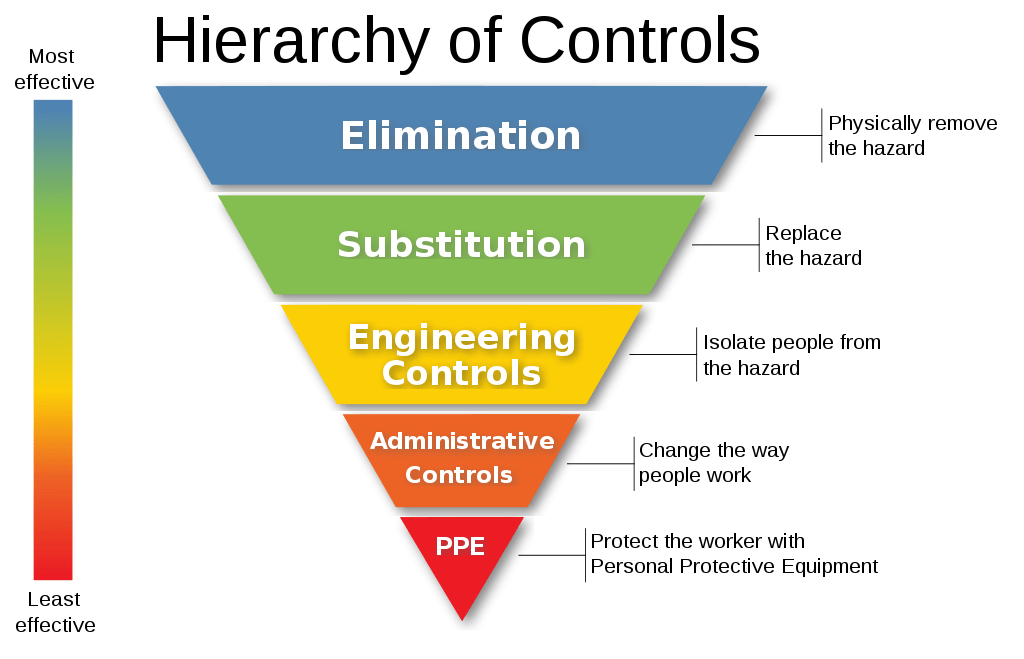
Elimination: Remove heat from the workplace during the designing stage, like designing the working area in such a way that the person is not exposed to steam or heat to avoid the risk of heat stress, i.e route steam or hot water line outside of the workplace. If elimination is not possible, apply other controls from the hierarchy of controls.
Substitution: Change the working location if the temperature is high. While working in an open atmosphere chose working time morning or evening instead of the afternoon to avoid exposure to high temperatures
Engineering control: In case substitution is not possible heat can be controlled by choosing the right engineering control
- Increased ventilation in the working area
- Provide cooling fans or air conditioners
- Use Local exhaust ventilation at the heat generation points
- Ensure hot surfaces are covered with insulations to avoid heat dissipation
- Avoid leaks of Hot utilities like steam, hot water, hot fluid, etc.
- Use a humidifier to maintain humidity or Misting fans to spray water droplets
Administrative controls
- Reduce working hours of employees working in a hot area
- Shorten exposure time and define time out of work after some hours of work based on working conditions (breaks for rest)
- Provide well-ventilated cool rest rooms with air-conditioned
- Provide cool drinking water, Lemon Juice, Energy drinks, electrolytes, etc. at strategic locations and restrooms
- Ensure the condition of the working area by continuous monitoring of temperature and humidity at the workplace
- Communicate the current condition of the workplace based on the heat index in case of condition changed
- Monitor employees to avoid heat-related illness
- Provide lightweight, light coloured, and cotton clothes to workers for comfortable working
- Adopt a work rotation policy to avoid long time exposure to the same workers
- Carried out preventive maintenance of all ventilation equipment regularly to avoid uncomforting during the breakdown
- Trained the workers on Heat stress symptoms, first aid, and controls
- Never force more production by neglecting heat stress
- Installed signages and display boards in the workplace to communicate hazards & controls related to heat stress
- Communicate the location of restrooms regularly in toolbox talks
- Emergency numbers and routes explain to workers in morning calls or induction
- Ensure no one consumes alcohol or caffeinated drinks while working in high temperature
- Prepare a detailed work plan to avoid heat-related illness at workplaces
- Lone working in High-temperature areas is strictly avoided
Personal Protective Equipment: PPE is the last level of defense it helps when all the above controls fail or after applying all possible controls still some level of risk exists, PPE can not reduce or control hazards.
Use following PPE to protect from heat stress
- Insulated suits
- Water-cooled clothing, suits, Jackets,
- Air-cooled suits
- Ice-cooled jackets, vests, neck wraps
- Light colour clothing with cotton fabric (breathable)
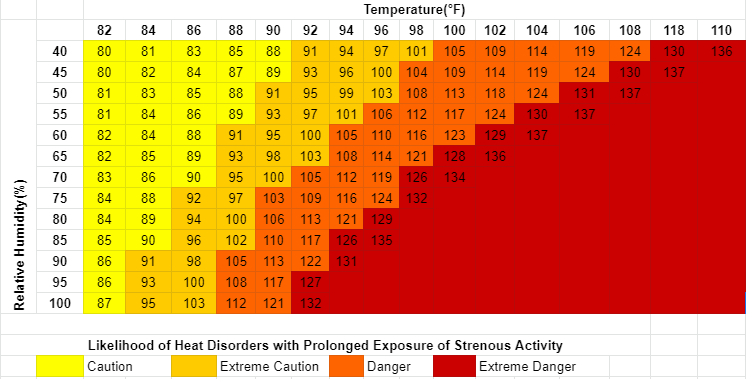
Heat Index for understanding
Heat index design by two parameters (1) Relative Humidity (%) & (2) Temperature (OF)
Both these parameters are continuously monitored by digital hygrometers or some portable temperature-humidity meters at the workplace and it displayed on screen live so anyone can easily observe both parameters
Score according to risk level
80-90 caution: Fatigue is possible if continued exposure, stay well hydrated, and restrict outdoors or working in the heat
91-103 Extreme caution: Heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stock are possible if continue working in this condition for a long time, reduce exposure time and keep yourself well hydrated by using 10 gulps of water every 20 min.
104-124 Danger: Heat stock is possible if continuously exposed to these conditions or else heat cramps, and heat exhaustion is possible
125 above Extreme Danger: High probability of Heat stock in this condition. So strictly avoid working if heat index numbers come above 125OF
Always work as per your ability to work in the heat. Gradually increase your working hours while working in heat sudden working for long hours leads to accidents so take time and increase working hours gradually to prepare the body as per conditions. Do not waste time during exposure to heat & take fast actions to avoid heat stocks
Conclusion: Pay Attention to Your Body When You Work in the Heat. Drink plenty of water
For videos related to safety follow us n Linkedin
for more toolbox talk click here…
To subscribe our newsletter share your mail id below

N/A
Excellent article, this is for work related heat stress which will be beneficial for those that work in the above mentioned industries.
How ever Heat stress is also appropriate for Leisure activities and general life and more needs to be done so that everyone has a understanding of the effect heat has on the human body, as you rightly say with global warming pushing up the temperatures.
Great info, thanks!
An excellent comprehensive article on an important subject.
Excellent! Thank you
Great! very informative and helpful.
Very educative. Thanks